Key Takeaways
- Phase angle, a reflection of whole-body cellular condition, is obtained using bioelectrical impedance analysis.
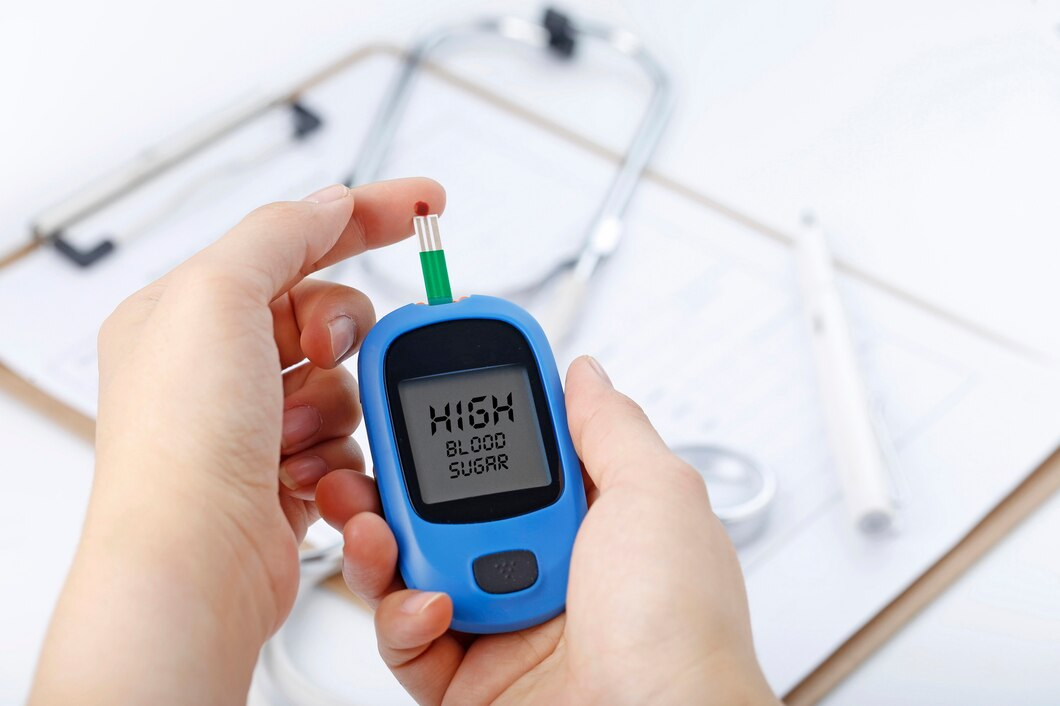
- Diabetic patients typically have a smaller phase angle compared to healthy individuals.
- Phase angle is negatively influenced by HbA1c.
- Various factors like HbA1c, age, sex, albumin level, and body mass index independently determine phase angle in diabetic participants.
- Phase angle offers a noninvasive insight into nutritional status, making it an invaluable tool in diabetes management.
Delving into Phase Angle
Phase angle (PhA), obtained from a non-invasive method called bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA), provides information about the overall health of cells and the body’s nutritional status. It is used in various fields, such as medicine, nutrition, and sports, and has become an important tool in health assessments.
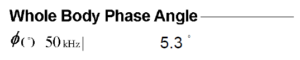
Understanding Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
BIA non-invasively measures body composition by applying a minor alternating current to the body and measuring the resultant impedance. Within this impedance, two primary components can be identified:
- Resistance (R): Represents resistance both inside and outside cells, predominantly from lipid components.
- Reactance (Xc): Denotes resistance specific to the cell membrane.
The Phase Angle serves as a valuable indicator of cellular health, reflecting the properties of the cell membrane and the balance of intra- and extracellular water. It is an invaluable tool in assessing and monitoring the overall health and nutritional status of individuals, particularly in diabetes management.
The Significance of Phase Angle
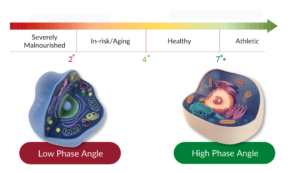
Phase angle remains unaffected by factors like body fluid, height, or weight. Instead, it provides a window into cellular health, reflecting the properties of the cell membrane and the balance of intra- and extracellular water. Positive correlations have been noted between PhA levels and nutritional indicators. Critically, low PhA levels have been linked to malnutrition, prolonged hospital stays, and even mortality in intensive care units.
Phase Angle’s Interplay with Diabetes
People with diabetes have lower PhA values than people without diabetes. This is because the high blood sugar in diabetics can damage cell membranes and impair their function. The severity of the decrease in PhA is related to the severity of diabetes and the degree of blood sugar control.
Diving into the Research
A retrospective study encompassing multiple centers was undertaken with Japanese diabetic patients. Utilizing BIA, body composition was analyzed, and phase angles were derived. The focus was on discerning the relationship between phase angle, clinical parameters, body composition, and HbA1c levels.
Key Outcomes of the Research
- Phase Angle & HbA1c: A negative influence of HbA1c on phase angle was evident (B = − 0.043, 95% Confidence interval: − 0.07 to − 0.02).
- For every 1% increase in HbA1c (which indicates higher blood sugar levels over time), the phase angle (a measure of cellular health) decreases by about 0.043 degrees.
Drawing Conclusions Phase angle’s capacity to serve as a straightforward, noninvasive metric of nutritional status becomes evident. Its potential as a crucial instrument in diabetes management cannot be understated.
For those seeking precision in measuring phase angles, InBody’s advanced BIA technology stands out. By providing accurate, non-invasive phase angle assessments, InBody aids healthcare professionals in elevating the care standard for diabetic patients.
The Practical Implications of Phase Angle in Diabetes Care
Incorporating Phase Angle in Routine Diabetic Assessments Given the relationship between Phase Angle and diabetes, incorporating PhA measurements into routine diabetes care can prove beneficial for several reasons:
- Comprehensive Health Status Indicator: Apart from just blood sugar levels, PhA offers a broader perspective on the overall health of the patient.
- Monitoring Treatment Efficacy: Changes in PhA can serve as indicators of how effective a treatment regimen is. For instance, improving PhA values might suggest enhanced cellular health resulting from the treatment.
- Predicting Complications: A declining PhA might be an early sign of complications, allowing timely interventions.
Phase Angle as a Nutritional Barometer in Diabetes
Diet plays a crucial role in managing diabetes. Given that PhA can be a reflection of nutritional status, it offers insights into the adequacy of nutrition in diabetic patients.
Factors Influencing PhA in Diabetics:
- Glycemic Control: Better controlled blood sugars can lead to improved PhA values, suggesting healthier cells.
- Dietary Quality: Diets rich in essential fatty acids, antioxidants, and micronutrients might promote healthier cell membranes, potentially resulting in a higher PA.
- Hydration: Since PhA reflects intra- and extracellular water conditions, any water retention due to inflammation can influence PhA values.
Optimizing Phase Angle Values: Recommendations for Diabetic Patients
- Routine PhA Measurements: Consider integrating regular PhA measurements into diabetes care. Devices like InBody provide reliable readings.
- Balanced Diet & Nutrition: Emphasize a nutritionally balanced diet with high fiber and rich in essential nutrients. This not only supports blood sugar control but may also positively impact PA.
- Staying Hydrated: Ensure adequate hydration levels, adjusting based on physical activity and other factors.
- Engaging in Regular Physical Activity: Exercise enhances cellular health and overall body function, potentially leading to improved PhA values.
- Continuous Monitoring: Regularly check other markers, like HbA1c, to ensure holistic diabetes management.
[Disclaimer: It’s always essential for patients to consult with healthcare professionals before making any changes to their routine or management strategies.]
Advanced Technologies & Phase Angle’s Future in Diabetes Management
InBody and the Revolution in Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis
The criticality of accurate Phase Angle measurements in diabetes management cannot be stressed enough. This is where cutting-edge technologies like those from InBody come to the fore:
- Precision: InBody’s BIA technology ensures that Phase Angle measurements are not just accurate but also consistent over time.
- User-friendly Interface: With a simple setup and user-friendly interface, InBody makes it possible even for individuals without technical expertise to obtain their Phase Angle measurements.
- Integration with Medical Systems: With compatibility for integration into broader healthcare systems, InBody devices can be an invaluable addition to clinical settings, ensuring that data is seamlessly incorporated into patients’ medical records.
Contact our team today to further understand how InBody can be an invaluable addition to your clinical setting. Take the next step towards enhanced patient care and comprehensive health management.
Final Thoughts
The use of Phase Angle in diabetes management represents the combination of technology and holistic health management. As we keep innovating, tools like InBody not only improve our current abilities but also create opportunities for the future. Phase Angle, with its non-invasive nature and deep insights, is ready to change not only diabetes management but also healthcare in general.
This research summary is a valuable resource for healthcare professionals, researchers, and individuals seeking to enhance their knowledge of diabetes management. It highlights the significance of phase angle in diabetes care and the practical implications of incorporating phase angle measurements into routine assessments.
Don’t miss out on this opportunity to expand your knowledge and enhance your approach to diabetes management. Click here to download the PDF and take the next step towards comprehensive health management.