Outline
- What is Phase Angle?
- Research Insights on Phase Angle and Muscular Performance
- Why is Phase Angle Crucial for Athletes?
- Maximizing Performance with Phase Angle
- Injury Recovery Tracking and Enhanced Rehabilitation
- Actionable Tips for Improving Phase Angle
- Concluding Thoughts: The Transformative Impact of Phase Angle
In the realm of elite sports, achieving and maintaining peak performance is a multifaceted endeavor. Athletes and coaches constantly seek innovative methods to enhance performance, optimize recovery, and prevent injuries.
Among the various metrics and tools at their disposal, one that stands out for its unique insights is the measurement of Phase Angle (PA). This blog post delves into the significance of Phase Angle for athletes, offering essential tips for leveraging this metric for improved performance and recovery.

What is Phase Angle?
Phase Angle is a key metric derived from Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA), a method used by high-tech devices like InBody. It measures the integrity of body cells and quantity of an athlete’s lean body mass, reflecting the health of their cells and tissues. In simple terms, Phase Angle provides a snapshot of an athlete’s cellular health, which is a cornerstone of their overall physical condition.
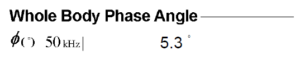
Research Insights on Phase Angle and Muscular Performance
Recent research further underscores the significance of Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis (BIA)-derived Phase Angle (PhA) in assessing muscular performance among athletes.
A comprehensive study involving 117 adult athletes from diverse sports backgrounds examined the correlation between whole-body PhA and muscular performance. Key performance metrics, including handgrip strength and countermovement jump power, were evaluated in relation to both WB and regional PhA, alongside lean soft tissue measurements obtained via BIA and dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry.
The findings were revealing: whole-body PhA showed a positive association with both relative power and relative absolute strength, independent of lean soft tissue.

Why is Phase Angle Crucial for Athletes?
- Muscle Quality Assessment: The Phase Angle is an indicator of muscle health and function. For athletes, a higher Phase Angle is typically associated with better muscle quality, which is crucial for strength, endurance, and performance.
- Training and Recovery Insights: Monitoring changes in Phase Angle can help in assessing the impact of training regimes and recovery strategies. A decreasing Phase Angle might suggest inadequate recovery, or emerging health issues.
- Nutritional Evaluation: When Phase Angle and muscle mass remain stagnant, it could suggest that the dietary plan was not adhered to as strictly as the training regimen required. Nutritional evaluation, including the optimization of dietary plans based on Phase Angle, becomes crucial to ensure the body receives the appropriate balance of nutrients for effective muscle development and recovery.
Maximizing Performance with Phase Angle
Athletes with a higher Phase Angle generally have better cellular health, which correlates with greater and stronger muscle mass. Athletes looking to maximize their performance can benefit significantly from monitoring their Phase Angle. Here are some ways to use Phase Angle data effectively:
- Personalized Training Programs: Understanding individual variations in cellular health can lead to customized training programs that cater to specific needs and goals.
- Optimized Recovery Strategies: Phase Angle can indicate the body’s state of stress and recovery. Athletes can use this data to tailor their recovery protocols, ensuring adequate rest and recuperation.
- Nutritional Adjustments: Regular monitoring of Phase Angle can signal the need for nutritional adjustments. Athletes can work with nutritionists to modify their diet, focusing on nutrients that enhance cellular health and performance.

Injury Recovery Tracking and Enhanced Rehabilitation
Phase Angle is not only related to sports performance, but it is also a crucial tool for tracking the progress and effectiveness of injury recovery and rehabilitation. Here is how Phase Angle can be utilized in these areas:
- Phase Angle as an Indicator of Injury Recovery: An increasing Phase Angle can be an early indicator of improvement for injury, allowing the health practitioner to know that the athletes are complying with the rehab instructions.
- Tailored Rehabilitation Programs: If the phase angle is declining or not improving, it could indicate that the current rehab routine is not suitable for the athletes. Monitoring the phase angle during the recovery process can help design rehabilitation programs that promote faster and more effective healing.
- Return-to-Play Decisions: Accurate assessment of an athlete’s readiness to return to play post-injury is crucial. Phase Angle measurements can provide objective data to support these decisions.

Actionable Tips for Improving Phase Angle
Improving Phase Angle is synonymous with enhancing cellular health, muscle quality, and overall physical well-being. Athletes can take several actionable steps to positively influence their Phase Angle readings:
- Balanced and Nutrient-Dense Diet: Focus on a diet rich in nutrients that support cellular health, including antioxidants, healthy fats, and adequate proteins. Hydration is equally crucial.
- Regular Strength and Conditioning Training: Incorporate a balanced mix of strength, endurance, and flexibility training to enhance muscle quality and overall physical health.
- Adequate Rest and Recovery: Prioritize rest and recovery, including quality sleep, rest days, and active recovery sessions, to allow the body to repair and strengthen.
- Stress Management: Chronic stress can negatively impact cellular health. Engage in stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or other relaxation practices.
- Regular Health Check-ups: Besides tracking Phase Angle, regular health check-ups can provide a comprehensive view of an athlete’s health status and inform adjustments in training and lifestyle.

Concluding Thoughts: The Transformative Impact of Phase Angle
Understanding and utilizing Phase Angle can be a game-changer for athletes at all levels. This metric offers a deeper insight into the body’s inner workings, going beyond traditional measures of fitness and performance. By focusing on improving their Phase Angle, athletes can enhance their performance, speed up recovery, prevent injuries, and potentially extend their sports careers.
Regular monitoring of Phase Angle, combined with tailored training and recovery strategies, can help athletes stay at the top of their game. The integration of this metric into sports regimes signifies a move towards more personalized and effective athletic training and health management.
In conclusion, Phase Angle is more than just a number; it’s a reflection of an athlete’s overall health and a predictor of their athletic potential. By embracing this powerful tool, athletes and coaches can unlock new levels of performance and longevity in sports.



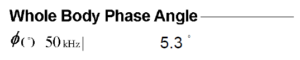
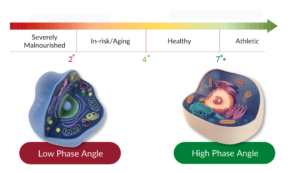

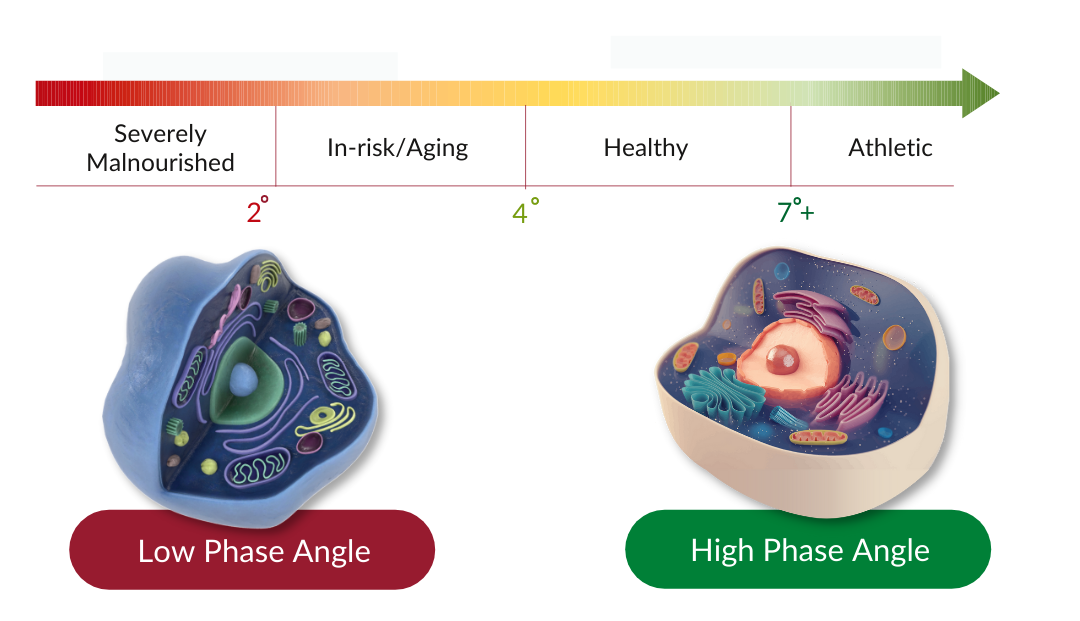
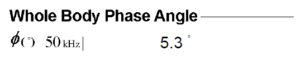
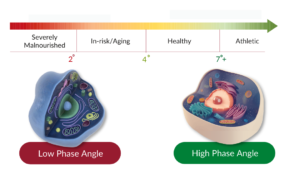
 Phase Angle results aren’t standalone figures. They are best interpreted by comparing them with reference values. A higher Phase Angle compared to the average population (>50th percentile) usually means you have healthier cell status and body composition.
Phase Angle results aren’t standalone figures. They are best interpreted by comparing them with reference values. A higher Phase Angle compared to the average population (>50th percentile) usually means you have healthier cell status and body composition.





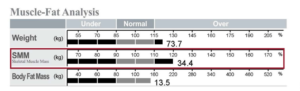




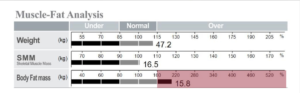 According to the image above, which is part of the sample printed result sheet, this normal weight child has a higher Body Fat Mass than the normal range according to the child’s gender and height.
According to the image above, which is part of the sample printed result sheet, this normal weight child has a higher Body Fat Mass than the normal range according to the child’s gender and height.