Why is body composition analysis an
effective tool for treating cardiovascular diseases?
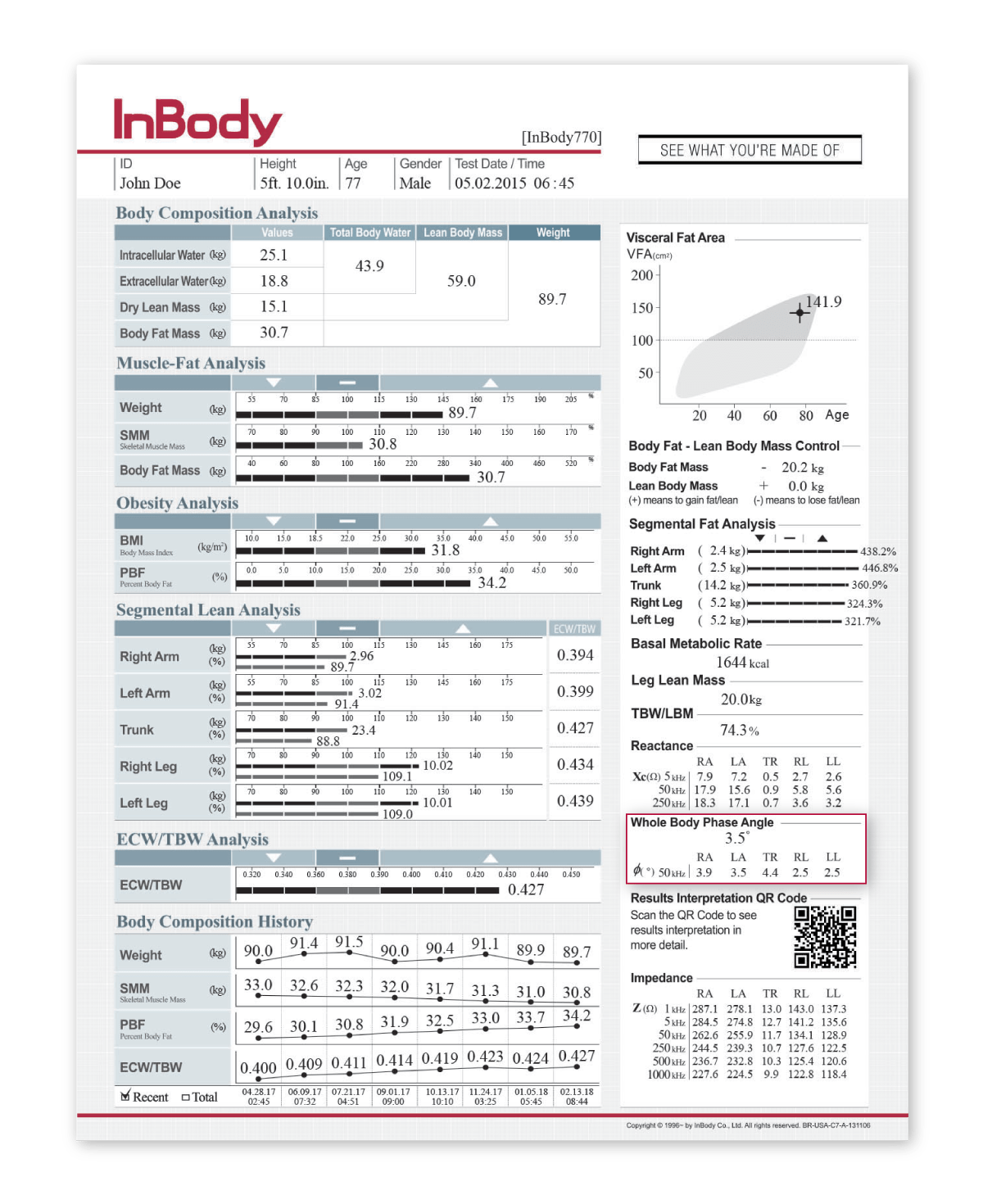
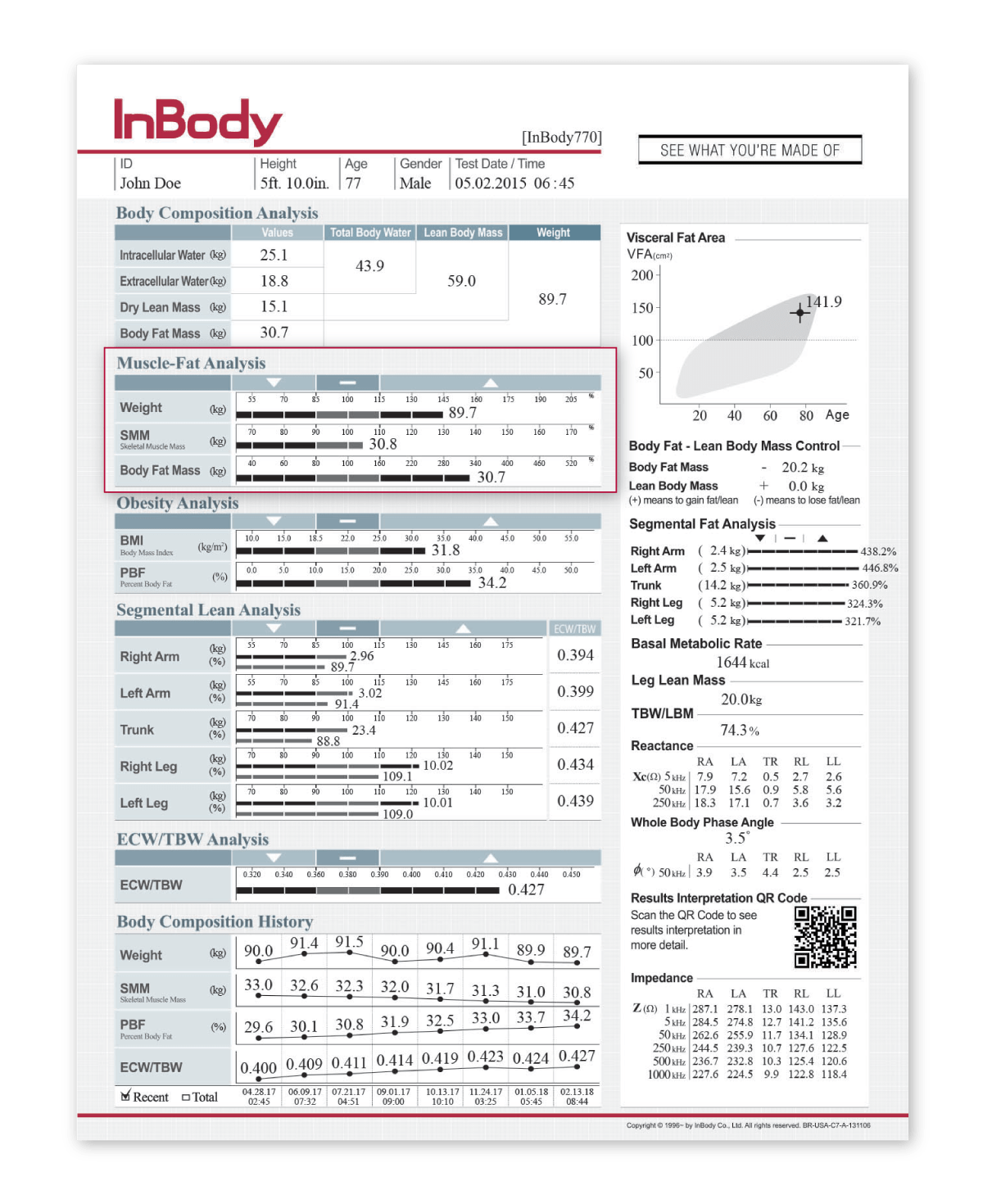
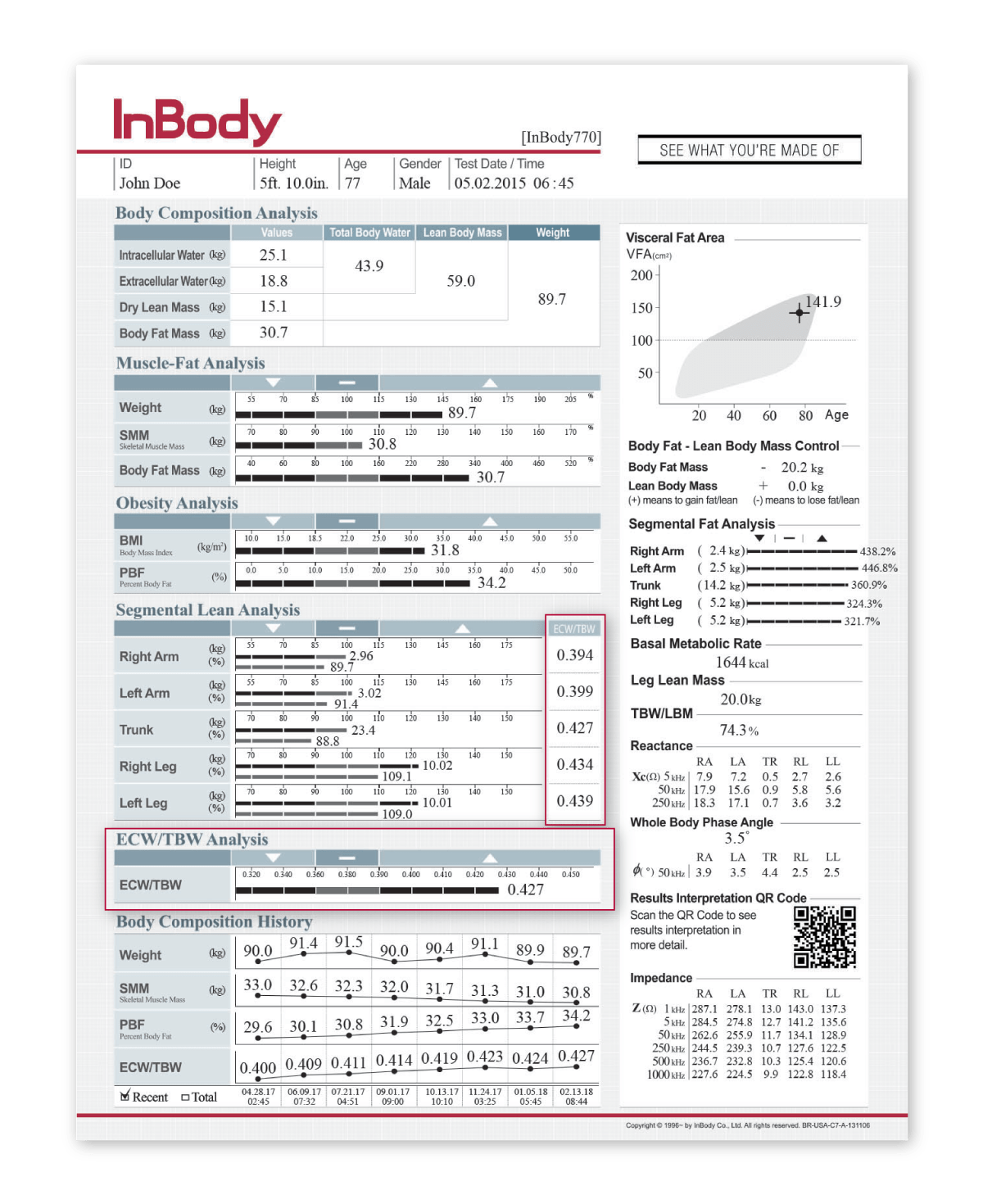
Body composition is important for understanding a patient’s cardiovascular health. High blood volume, increased water levels in the body, strains on the heart are all issues that stem from conditions like obesity. BMI is commonly used to determine a patient’s risk for cardiovascular disease; however, BMI overlooks a patients’ visceral fat that is often linked to a higher risk for cardiovascular risk. By using this method, doctors cannot determine how much of a patient’s body is muscle or fat.
On the other hand, body composition analysis differentiates between a patient’s muscle, fat, and water levels. Studies have proven InBody DSM-BIA body composition analyzers are an effective tool for treating patients with cardiovascular disease and improving surgical outcomes. InBody devices ensure cardiology professionals can be certain that the outputs generated accurately reflect changes within the patient.
In less than 60 seconds, cardiology professionals receive an InBody Result Sheet (body composition printout) that can aid in:
– Obtaining objective fluid measures and guide fluid management strategies
– Effectively monitoring nutrition status and guide nutritional interventions
– Accurately tracking patient progress and predict surgical outcomes