Study 1
HIGH CORRELATION WITH DEXA FOR LEAN MASS MEASUREMENTS
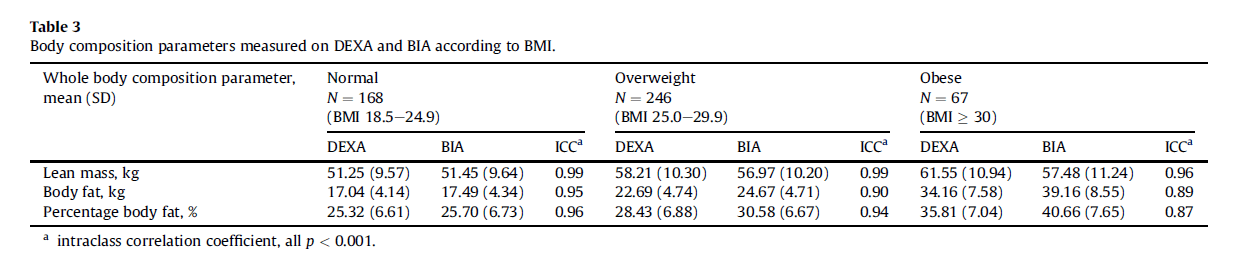
A 2011 study published by Clinical Nutrition compared the accuracy of DSM-BIA (InBody 720) against DXA with 484 middle-aged participants. The study found that the InBody had a 99% correlation to DXA when measuring lean mass in normal and overweight populations. “In conclusion, this study shows DSM-BIA to be a valid tool for the assessment of whole body composition and segmental lean mass measurements in middle-aged population when validated against DEXA“
Ling, Carolina H. Y.; de Craen, Anton J. M.; Slagboom, Pieternella E.; Gunn, Dave A.; Stokkel, Marcel P. M.; Westendorp, Rudi G. J.; Maier, Andrea B. (2011-10). “Accuracy of direct segmental multi-frequency bioimpedance analysis in the assessment of total body and segmental body composition in middle-aged adult population”. Clinical Nutrition (Edinburgh, Scotland). 30 (5): 610–615. doi:10.1016/j.clnu.2011.04.001. ISSN 1532-1983. PMID 21555168.
Study 2
ACCURATE BODY WATER MEASUREMENTS REGARDLESS OF BODY SIZE
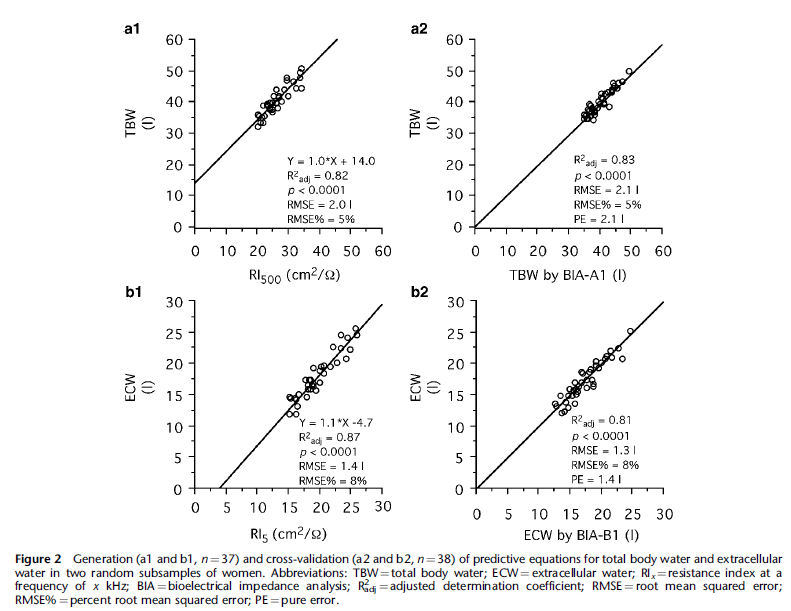
A 2005 cross-validation study published by the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition evaluated the accuracy of eight-polar bioelectrical impedance analysis for the assessment total body water (TBW) and extracellular water (ECW) in severe obesity. The InBody 3.0’s results were compared to results found from the Br dilution method. The study concluded that the InBody offered accurate estimates of TBW and ECW without the need for population-specific formulas or empirical equations.
Sartorio, A.; Malavolti, M.; Agosti, F.; Marinone, P. G.; Caiti, O.; Battistini, N.; Bedogni, G. (February 2005). “Body water distribution in severe obesity and its assessment from eight-polar bioelectrical impedance analysis”. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 59(2): 155–160. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1602049. ISSN 0954-3007. PMID 15340370.
Study 3
HIGH ACCURACY OF BODY FAT MEASURES IN HEALTHY POPULATIONS
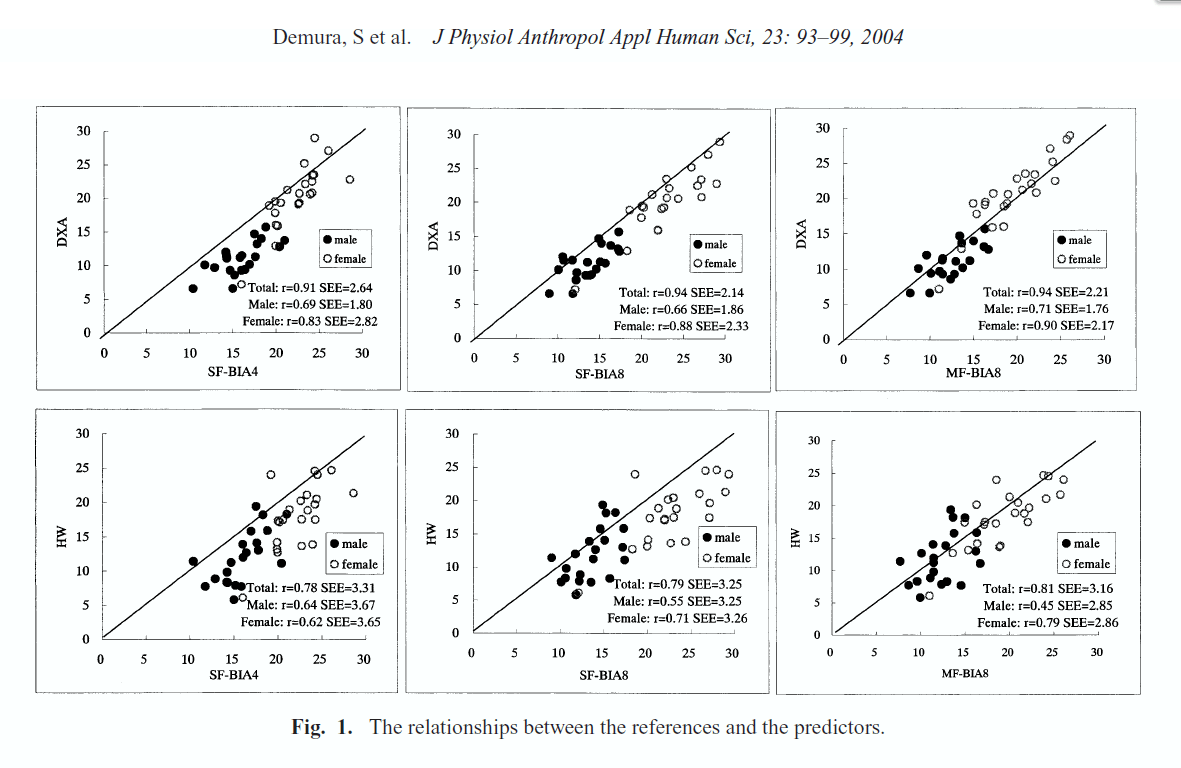
A 2004 study published by the Journal of Physiological Anthropology and Applied Human Science compared the accuracy of three BIA devices (Tanita BC-118 [SF-BIA4], Tanita TBF-101 [SF-BIA8], InBody 3.0 [MF-BIA8]) against DXA and hydrostatic weighing. The study concluded that the InBody 3.0 (referred to as MF-BIA8) showed the highest correlation in results to DXA and hydrostatic weighing and showed the least estimation error compared to the other BIA methods (94% correlation with DXA and 81% correlation with hydrostatic weighing).
Demura, Shinichi; Sato, Susumu; Kitabayashi, Tamotsu (2004). “Percentage of Total Body Fat as Estimated by Three Automatic Bioelectrical Impedance Analyzers”. Journal of PHYSIOLOGICAL ANTHROPOLOGY and Applied Human Science. 23 (3): 93–99. doi:10.2114/jpa.23.93. ISSN 1345-3475.
Study 4
HIGH ACCURACY AND EASE OF USE AS A FIELD-BASED ASSESSMENT TOOL
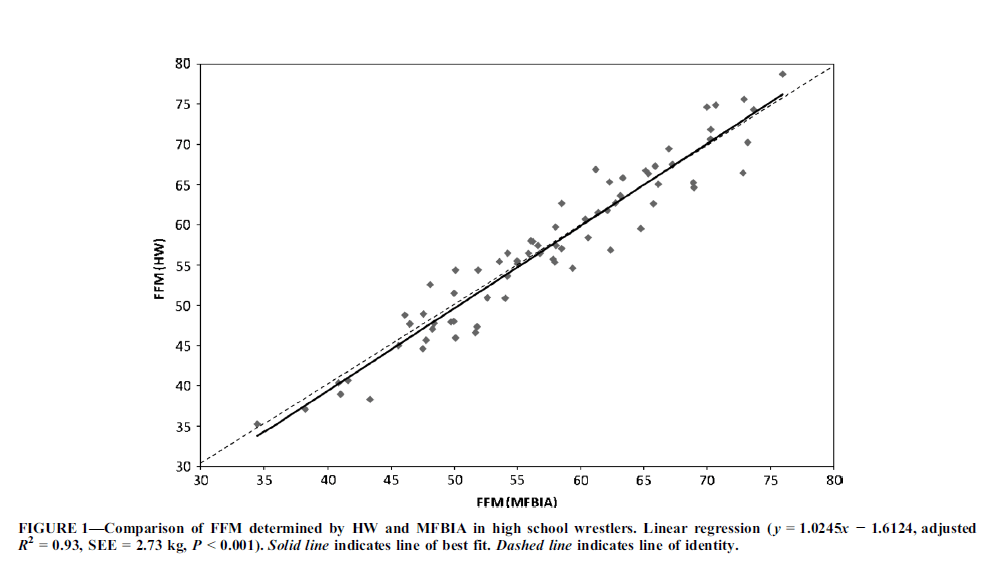
A study published in 2010 found results from the InBody 520 to be highly correlated with fat-free mass (FFM) measures from hydrostatic weighing (96%). The study also concluded that the InBody does not require a high degree of technical skill, making it easy to use and safe, and also provides simultaneous measures of body mass, body composition, and TBW in a short period of time. “These advantages may make MFBIA attractive to educational institutions that may not have access to trained anthropometrists, HW, ADP, and DXA and to address concerns that have been expressed by coaches, officials, and athletic trainers who question the results of SK testing performed by someone who may not be completely objective or impartial.”
UTTER, ALAN C.; LAMBETH, PAMELA G. (2010-02). “Evaluation of Multifrequency Bioelectrical Impedance Analysis in Assessing Body Composition of Wrestlers”. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise. 42(2): 361–367. doi:10.1249/mss.0b013e3181b2e8b4. ISSN 0195-9131.
Study 5
HIGH ACCURACY OF BOTH TOTAL AND SEGMENTAL LEAN BODY MASS IN YOUNG CHILDREN
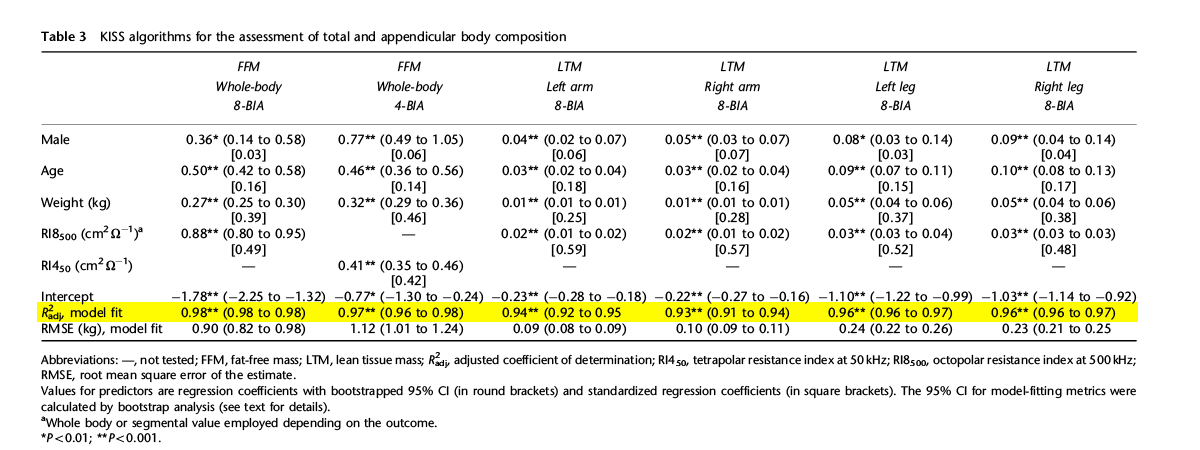
A 2009 cross-validation study published by the European Journal of Clinical Nutrition compared the accuracy of tetra (RJL Systems model 101A) and octopolar (InBody 3.0) bioelectrical impedance analysis against DXA for the assessment of total and appendicular body composition in children. The study concluded that the InBody 3.0 was superior to BIA devices that use only 4 electrodes for the prediction of FFM, that empirical estimations tetrapolar BIA devices used gave biased predictions of FFM, and that InBody was an accurate predictor of segmental body composition.
Kriemler, S.; Puder, J.; Zahner, L.; Roth, R.; Braun-Fahrländer, C.; Bedogni, G. (2009-5). “Cross-validation of bioelectrical impedance analysis for the assessment of body composition in a representative sample of 6- to 13-year-old children”. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 63 (5): 619–626. doi:10.1038/ejcn.2008.19. ISSN 1476-5640. PMID 18285806.
Study 6
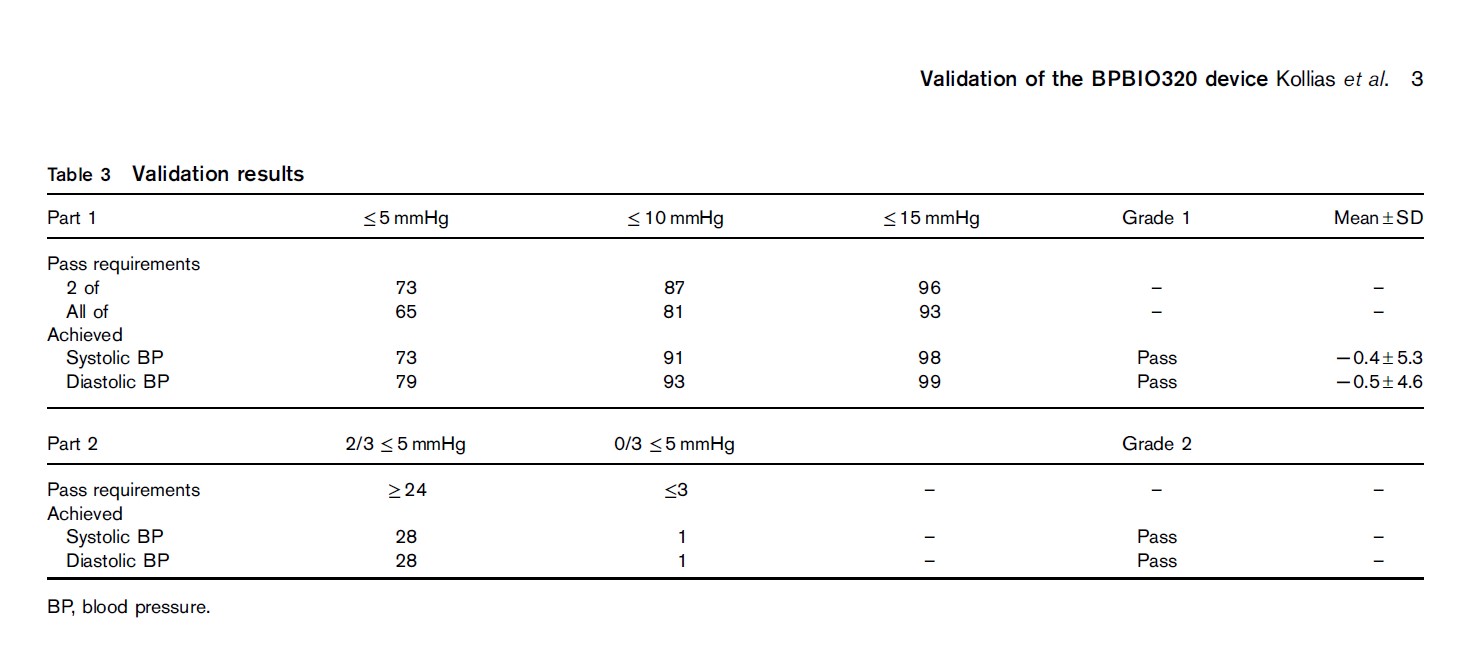
BLOOD PRESSURE MONITOR VALID FOR CLINICAL USE
“The single-cuff oscillometric device InBody BPBIO320 developed for self-measurement by adults in public spaces passed all the validation requirements of the 2010 ESH-IP and can be recommended for clinical use.” The test–reference BP difference was 0.5±4.3/−1.1±4.3mmHg (systolic/diastolic) in participants with arm circumference less than 31.4 cm (n=17) and −1.3±6.0/0.2±4.8mmHg in those with an arm circumference of at least 31.4 cm (n=16). This indicates that the margin of error is ~5/5.5 mmHg (systolic/diastolic) in those with smaller arms, and ~7/5 mmHg (systolic/diastolic) in those with higher arm circumference.
Kollias, A., Stambolliu, E., Kyriakoulis, K. G., Papadatos, S. S., & Stergiou, G. S. (2019). Validation of the single-cuff oscillometric blood pressure monitor InBody BPBIO320 for public use according to the 2010 European Society of Hypertension International Protocol. Blood pressure monitoring, 24(1), 30-32.